Lipoprotein b
What does a high apo B mean? Apolipoprotein B is the primary apolipoprotein of chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, and LDL particles (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer bad cholesterol when in reference to both heart disease and vascular disease in general), which is responsible for carrying fat molecules (lipids), including cholesterol, around the body (within the water outside cells) to all cells within all tissues. How to lower apo B? Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) is an important component of many lipoproteins that are involved in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis may be described as a chronic inflammation in the arterial wall. A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly whose primary purpose is to transport hydrophobic lipid (also known as fat) molecules in water, as in blood plasma or other extracellular fluids.
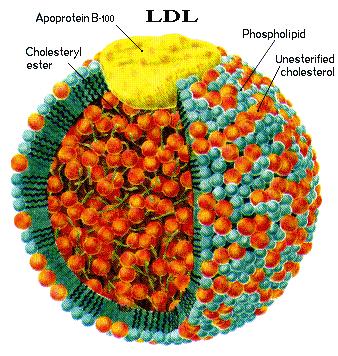
Apolipoprotein B Apolipoprotein B measurement does serve a useful purpose in the investigation of lipid disorders. As there is only one apo B molecule in each apo B containing lipoprotein particle, measurement of apo B provides a measure of particle number. LDL pattern B simply means that you have a substantial proportion of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles (often wrongly called LDL cholesterol ) that are abnormally small.
If you have mostly. Apolipoprotein B test (ApoB) is an essential test which is a constituent of various lipoproteins which are involved in cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. The chronic inflammation in the arterial wall is known as atherosclerosis.
ApoBs are proteins found in lipoprotein particles that are artery-clogging. The apoB-containing lipoprotein particles that are the most damaging to our arteries include not only LDL cholesterol but also remnants of chylomicrons and VLDL (very low density lipoproteins ). All three – LDL, VLDL, and chylomicrons – promote atherosclerosis.
Apolipoprotein B-1(also called apolipoprotein B or apo B ) is a protein that is involved in the metabolism of lipids and is the main protein constituent of lipoproteins such as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL, the bad cholesterol). This test measures the amount of apo B in the blood. Lipoprotein (a) or LP(a) for short is a large lipoprotein particle made by the liver. It consists of a particle similar to LDL and protein molecules known as ApoB and Apo(a).
A special blood test called polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis can measure particle size and determine whether a person has blood cholesterol LDL pattern A or LDL pattern B. Persons with LDL cholesterol pattern A have large, buoyant LDL cholesterol particles. Apolipoprotein B1(apoB100) is the primary protein in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. The LDL complex is the principal vehicle for delivering cholesterol to body tissues through the blood. The apoB1test measures the amount of this type of cholesterol in the blood. Lipoproteins are special particles made up of droplets of fats surrounded by a single layer of phospholipid molecules.
Phospholipids are molecules of fats which are attached to a. LDL (low-density lipoprotein), sometimes called “bad” cholesterol, makes up most of your body’s cholesterol. High levels of LDL cholesterol raise your risk for heart disease and stroke. HDL (high-density lipoprotein), or “good” cholesterol, absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver.
The liver then flushes it from the body. As food is digested after a meal, chylomicrons are formed to carry fat and cholesterol from the intestine into the bloodstream. Some people are genetically predisposed to have a lot of lipoprotein (a) and others very little.
Quantitate Human Apo lipoprotein B with 5. Elevated lipoprotein (a) is a genetic condition.
A healthcare provider cannot tell if a patient has elevated lipoprotein (a) by examining them.
Comments
Post a Comment